Hadoop 生态圈(二十五)- MapReduce Join 操作
|字数总计:3.4k|阅读时长:13分钟|阅读量:
前言
部分内容摘自尚硅谷、黑马等等培训资料
1. 背景
在实际的数据库应用中,我们经常需要从多个数据表中读取数据,这时我们就可以使用 SQL 语句中的连接(JOIN),在两个或多个数据表中查询数据。
在使用 MapReduce 框架进行数据处理的过程中,也会涉及到从多个数据集读取数据,进行join关联的操作,只不过此时需要使用 java 代码并且根据 MapReduce 的编程规范进行业务的实现。
但是由于 MapReduce 的分布式设计理念的特殊性,因此对于 MapReduce 实现 join 操作具备了一定的特殊性。特殊主要体现在:究竟在MapReduce中的什么阶段进行数据集的关联操作,是mapper阶段还是reducer阶段,之间的区别又是什么?
整个 MapReduce 的 join 分为两类:map side join、reduce side join。
2. reduce side join
2.1 概述
reduce side join,顾名思义,在reduce阶段执行join关联操作。这也是最容易想到和实现的 join 方式。因为通过shuffle过程就可以将相关的数据分到相同的分组中,这将为后面的 join 操作提供了便捷。
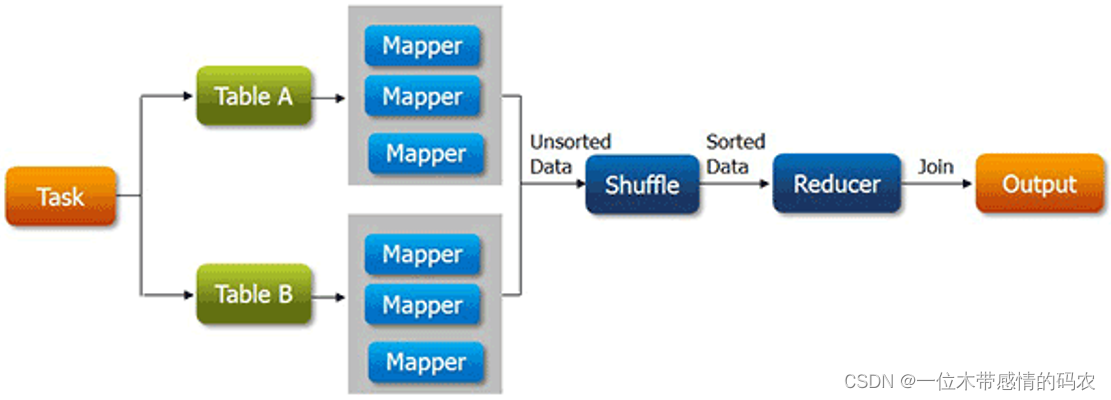
基本上,reduce side join大致步骤如下:
- mapper 分别读取不同的数据集;
- mapper 的输出中,通常以 join 的字段作为输出的 key;
- 不同数据集的数据经过 shuffle,key 一样的会被分到同一分组处理;
- 在 reduce 中根据业务需求把数据进行关联整合汇总,最终输出。
2.2 弊端
reduce 端 join 最大的问题是整个 join 的工作是在 reduce 阶段完成的,但是通常情况下 MapReduce 中 reduce 的并行度是极小的(默认是 1 个),这就使得所有的数据都挤压到reduce阶段处理,压力颇大。虽然可以设置 reduce 的并行度,但是又会导致最终结果被分散到多个不同文件中。
并且在数据从 mapper 到 reducer 的过程中,shuffle阶段十分繁琐,数据集大时成本极高。
3. MapReduce分布式缓存
DistributedCache 是 hadoop 框架提供的一种机制,可以将job指定的文件,在job执行前,先行分发到task执行的机器上,并有相关机制对cache文件进行管理。
DistributedCache 能够缓存应用程序所需的文件 (包括文本,档案文件,jar 文件等)。
Map-Redcue 框架在作业所有任务执行之前会把必要的文件拷贝到 slave 节点上。 它运行高效是因为每个作业的文件只拷贝一次并且为那些没有文档的 slave 节点缓存文档。
3.1 使用方式
3.1.1 添加缓存文件
可以使用 MapReduce 的 API 添加需要缓存的文件。
1
2
3
4
|
job.addCacheArchive(URI uri);
job.addCacheFile(URI uri);
|
注意:需要分发的文件,必须提前放到hdfs上,默认的路径前缀是hdfs://。
3.1.2 程序中读取缓存文件
在 Mapper 类或者 Reducer 类的 setup 方法中,用输入流获取分布式缓存中的文件。
1
2
3
4
5
| protected void setup(Context context) throw IOException,InterruptedException{
FileReader reader = new FileReader("myfile");
BufferReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
......
}
|
4. map side join
4.1 概述
map side join,其精髓就是在map阶段执行join关联操作,并且程序也没有了reduce阶段,避免了 shuffle 时候的繁琐。实现的关键是使用MapReduce的分布式缓存。
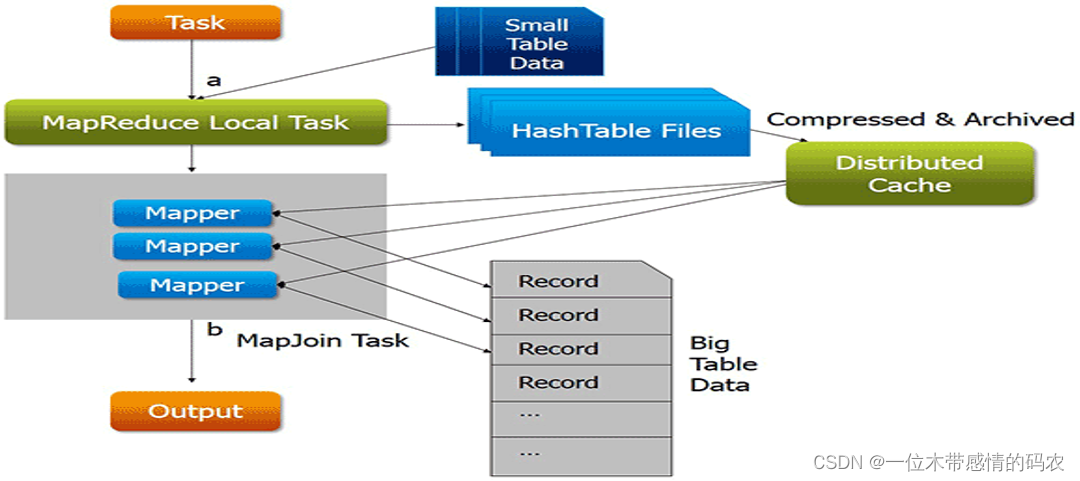
尤其是涉及到一大一小数据集的处理场景时,map 端的 join 将会发挥出得天独厚的优势。
map side join 的大致思路如下:
- 首先分析 join 处理的数据集,使用分布式缓存技术将小的数据集进行分布式缓存;
- MapReduce 框架在执行的时候会自动将缓存的数据分发到各个 maptask 运行的机器上;
- 程序只运行 mapper,在 mapper 初始化的时候从分布式缓存中读取小数据集数据,然后和自己读取的大数据集进行 join 关联,输出最终的结果;
- 整个 join 的过程没有 shuffle,没有 reducer;
4.2 优势
map 端 join 最大的优势减少 shuffle 时候的数据传输成本。并且 mapper 的并行度可以根据输入数据量自动调整,充分发挥分布式计算的优势。
5. MapReduce join案例:订单商品处理
5.1 需求
有两份结构化的数据文件:itheima_goods(商品信息表)、itheima_order_goods(订单信息表),具体字段内容如下。
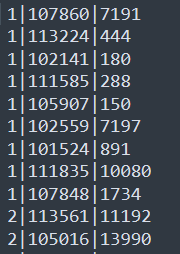
要求使用MapReduce统计出每笔订单中对应的具体的商品名称信息。比如107860商品对应着:AMAZFIT黑色硅胶腕带。
数据文件链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1W7lk7jA66bHC6-ShkxNeJQ ,提取码:6666
5.1.1 itheima_goods
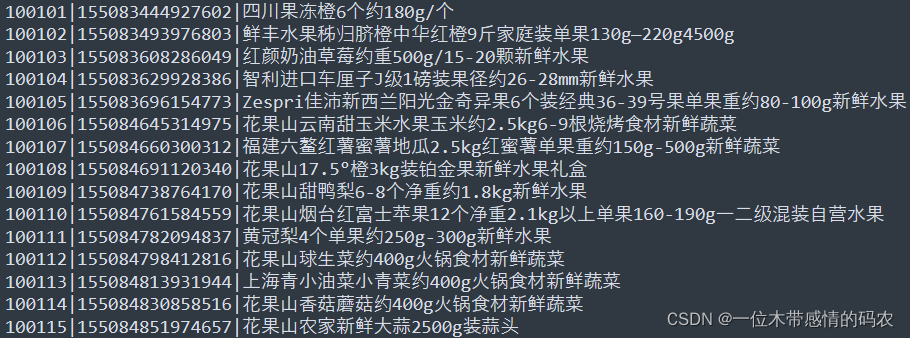
5.1.1 itheima_order_goods
5.2 Reduce Side实现
5.2.1 分析
使用 mapper 处理订单数据和商品数据,输出的时候以 goodsId 商品编号作为 key。相同 goodsId 的商品和订单会到同一个 reduce 的同一个分组,在分组中进行订单和商品信息的关联合并。在 MapReduce 程序中可以通过 context 获取到当前处理的切片所属的文件名称。根据文件名来判断当前处理的是订单数据还是商品数据,以此来进行不同逻辑的输出。
join 处理完之后,最后可以再通过 MapReduce 程序排序功能,将属于同一笔订单的所有商品信息汇聚在一起。
5.2.2 代码实现
5.2.2.1 mapper类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| public class ReduceJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text,Text> {
Text outKey = new Text();
Text outValue = new Text();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String filename =null;
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
filename = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
System.out.println("当前正在处理的文件是:"+filename);
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
sb.setLength(0);
String[] fields = value.toString().split("\\|");
if(filename.contains("itheima_goods.txt")){
outKey.set(fields[0]);
StringBuilder append = sb.append(fields[1]).append("\t").append(fields[2]);
outValue.set(sb.insert(0, "goods#").toString());
System.out.println(outKey+"---->"+outValue);
context.write(outKey,outValue);
}else{
outKey.set(fields[1]);
StringBuilder append = sb.append(fields[0]).append("\t").append(fields[2]);
outValue.set(sb.insert(0, "order#").toString());
System.out.println(outKey+"---->"+outValue);
context.write(outKey,outValue);
}
}
}
|
5.2.2.2 reducer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public class ReduceJoinReducer extends Reducer<Text,Text,Text,Text> {
List<String> goodsList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderList = new ArrayList<>();
Text outValue = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
if(value.toString().startsWith("goods#")){
String s = value.toString().split("#")[1];
goodsList.add(s);
}
if(value.toString().startsWith("order#")){
String s = value.toString().split("#")[1];
orderList.add(s);
}
}
int goodsSize = goodsList.size();
int orderSize = orderList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < orderSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < goodsSize; j++) {
outValue.set(orderList.get(i)+"\t"+goodsList.get(j));
context.write(key,outValue);
}
}
orderList.clear();
goodsList.clear();
}
}
|
5.2.2.3 程序主类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| public class ReduceJoinDriver extends Configured implements Tool {
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(getConf(), ReduceJoinDriver.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(ReduceJoinDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(ReduceJoinMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(ReduceJoinReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("D:\\datasets\\mr_join\\input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:\\datasets\\mr_join\\rjout"));
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
int status = ToolRunner.run(conf, new ReduceJoinDriver(), args);
System.exit(status);
}
}
|
5.2.2.4 结果排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| public class ReduceJoinSortApp {
public static class ReduceJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text,Text>{
Text outKey = new Text();
Text outvalue = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t");
outKey.set(fields[1]);
outvalue.set(fields[1]+"\t"+fields[0]+"\t"+fields[3]+"\t"+fields[4]+"\t"+fields[2]);
context.write(outKey,outvalue);
}
}
public static class ReduceJoinReducer extends Reducer<Text,Text,Text, NullWritable>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(value,NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, ReduceJoinSortApp.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(ReduceJoinSortApp.class);
job.setMapperClass(ReduceJoinMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(ReduceJoinReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("D:\\datasets\\mr_join\\rjout"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:\\datasets\\mr_join\\rjresult"));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 :1);
}
}
|
5.2.3 提交运行
直接在驱动类中右键运行 main 方法,使用 MapReduce 的本地模式执行。也可以将程序使用 maven 插件打包成 jar 包,提交到 yarn 上进行分布式运行。
- reduce join的结果
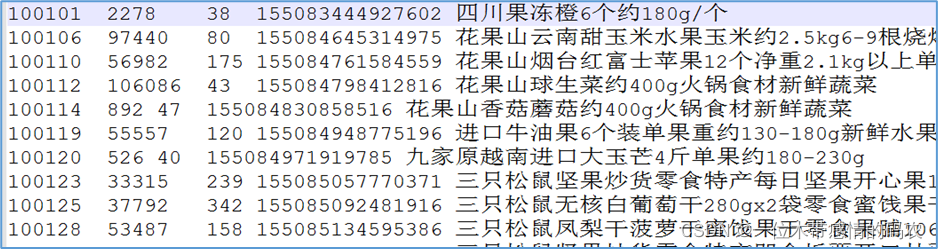
可以发现属于同一笔订单的商品信息被打散了。
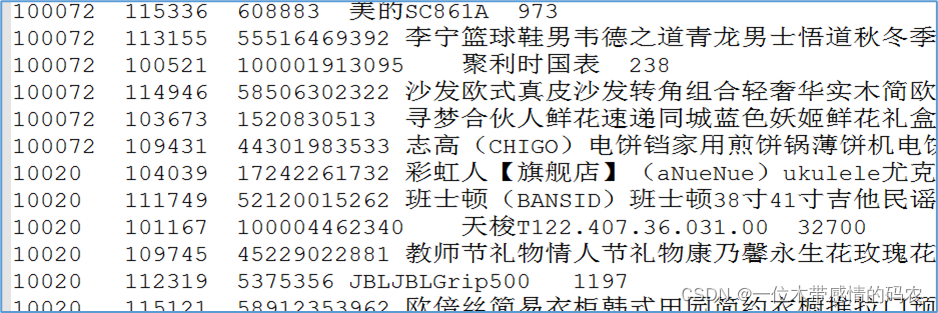
- 重新排序之后的结果
5.3 Map Side实现
5.3.1 分析
Map-side Join 是指在 Mapper 任务中加载特定数据集,此案例中把商品数据进行分布式缓存,使用 Mapper 读取订单数据和缓存的商品数据进行连接。
通常为了方便使用,会在 mapper 的初始化方法 setup 中读取分布式缓存文件加载的程序的内存中,便于后续 mapper 处理数据。
因为在 mapper 阶段已经完成了数据的关联操作,因此程序不需要进行 reduce。需要在 job 中将 reducetask 的个数设置为 0,也就是 mapper 的输出就是程序最终的输出。
5.3.2 代码实现
5.3.2.1 mapper类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class MapJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text, NullWritable> {
Map<String, String> goodsMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
Text k = new Text();
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("itheima_goods.txt")));
String line = null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
String[] fields = line.split("\\|");
goodsMap.put(fields[0], fields[1]+"\t"+fields[2]);
}
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] fields = value.toString().split("\\|");
String goodsInfo = goodsMap.get(fields[1]);
k.set(value.toString()+"\t"+goodsInfo);
context.write(k, NullWritable.get());
}
}
|
5.3.2.2 程序主类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class MapJoinDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, MapJoinDriver.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(MapJoinDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(MapJoinMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.addCacheFile(new URI("/data/join/cache/itheima_goods.txt"));
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/data/join/input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/data/join/mrresult"));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 :1);
}
}
|
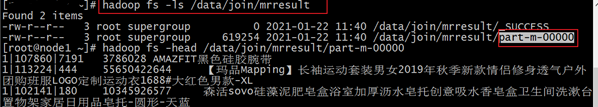
5.3.3 提交运行
分布式缓存的使用必须使用MapReduce的yarn模式运行。
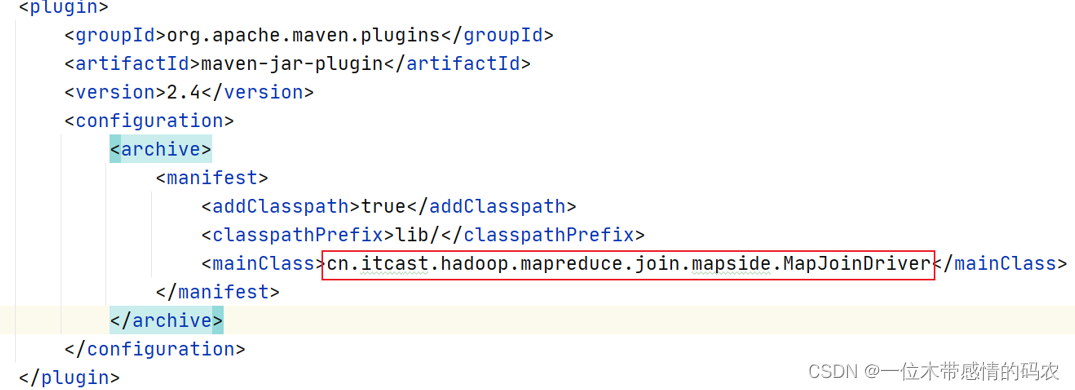
- 在工程的 pom.xml 文件中指定程序运行的主类全路径;
- 执行 mvn package 命令生成 jar 包;
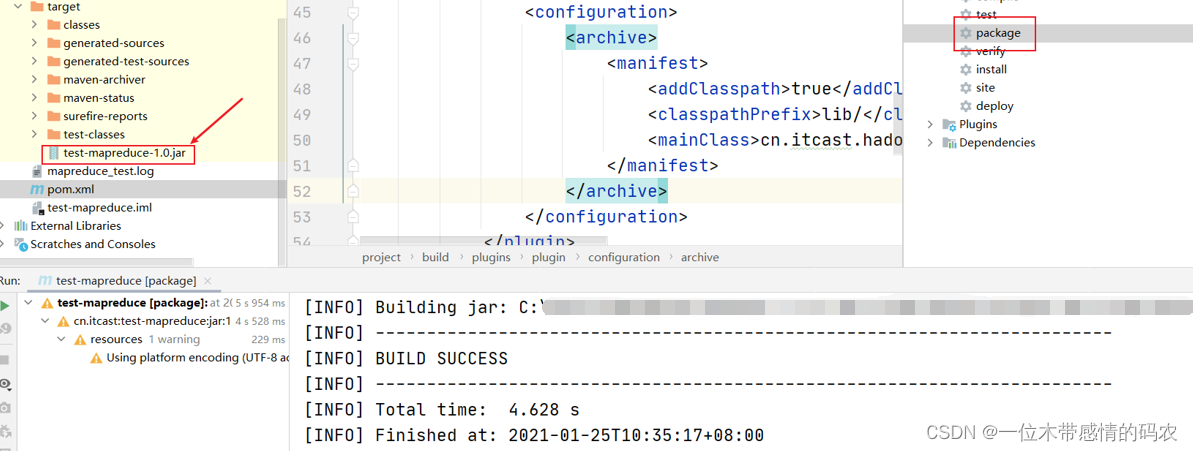
- 将 jar 包上传到 hadoop 集群(任意节点上);
- 执行命令(任意节点上):
hadoop jar xxxx.jar。注意保证 yarn 集群提前启动成功。
5.3.4 运行结果