Hadoop 生态圈(二十一)- MapReduce 编程基础
|字数总计:6.2k|阅读时长:26分钟|阅读量:
前言
部分内容摘自尚硅谷、黑马等培训资料
1. MapReduce Partition、Combiner
1.1 MapReduce Partition分区
1.1.1 默认情况下MR输出文件个数
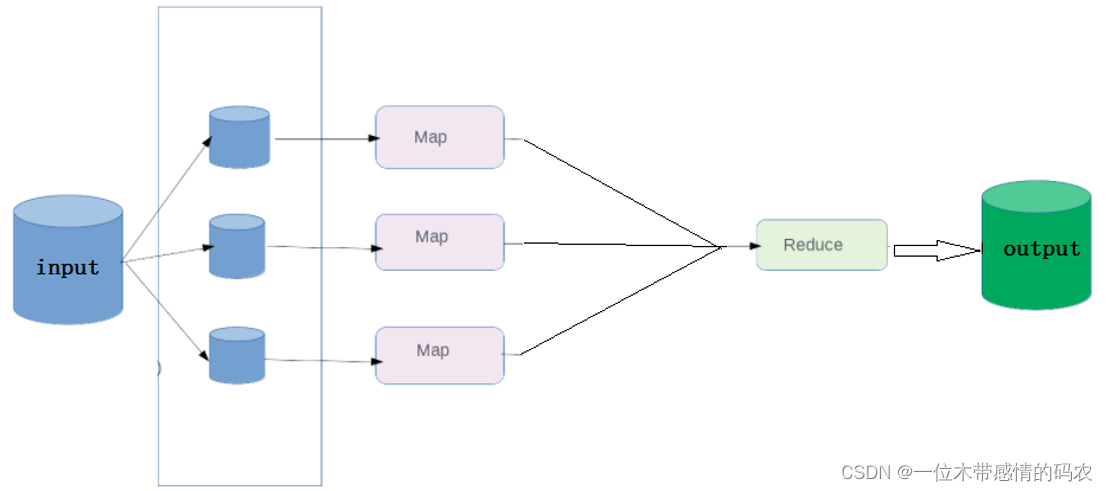
在默认情况下,不管 map 阶段有多少个并发执行 task,到 reduce 阶段,所有的结果都将有一个 reduce 来处理,并且最终结果输出到一个文件中。
此时,MapReduce 的执行流程如下所示:
1.1.2 修改reducetask个数
在 MapReduce 程序的驱动类中,通过 job 提供的方法,可以修改 reducetask 的个数。
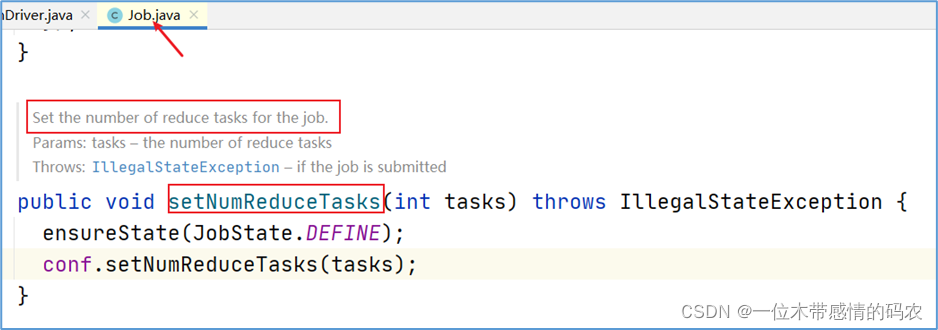
默认情况下不设置,reducetask 个数为 1,结果输出到一个文件中。
使用 api 修改 reducetask 个数之后,输出结果文件的个数和reducetask个数对应。比如设置为 6 个,此时的输出结果如下所示:
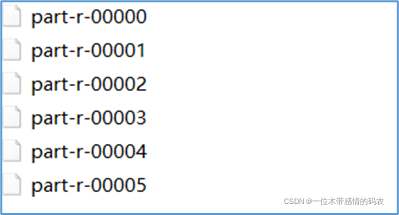
此时,MapReduce 的执行流程如下所示:
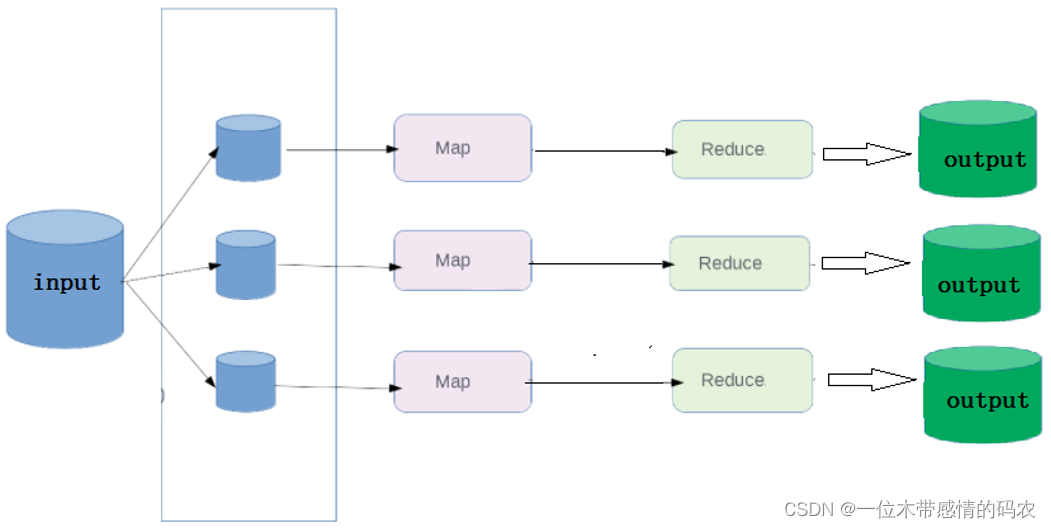
1.1.3 数据分区概念
当 MapReduce 中有多个reducetask执行的时候,此时maptask的输出就会面临一个问题:究竟将自己的输出数据交给哪一个reducetask来处理,这就是所谓的数据分区(partition)问题。
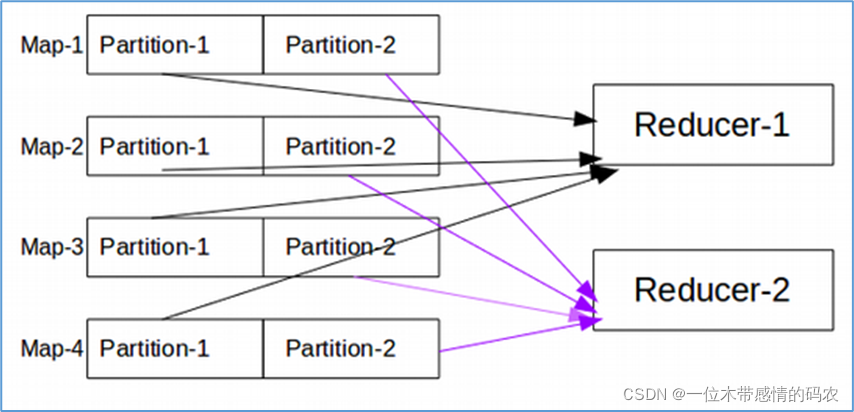
1.1.4 默认分区规则
MapReduce 默认分区规则是HashPartitioner。跟 map 输出的数据 key 有关。
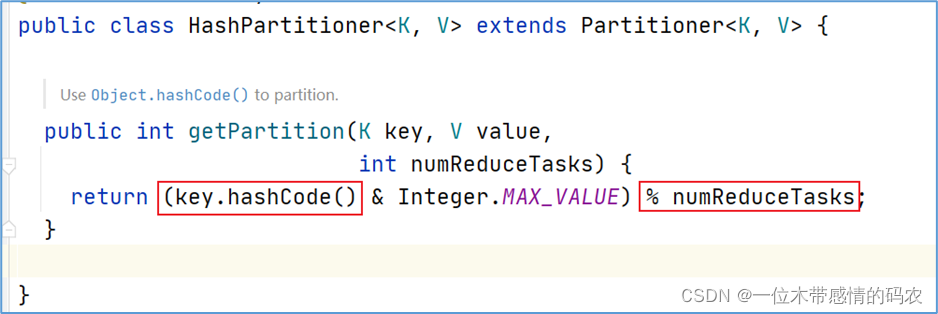
当然用户也可以自己自定义分区规则。
1.1.5 Partition注意事项
reducetask个数的改变导致了数据分区的产生,而不是有数据分区导致了 reducetask 个数改变。- 数据分区的核心是分区规则。即如何分配数据给各个 reducetask。
- 默认的规则可以保证只要
map阶段输出的key一样,数据就一定可以分区到同一个reducetask,但是不能保证数据平均分区。
- reducetask 个数的改变还会导致输出结果文件不再是一个整体,而是输出到多个文件中。
1.2 MapReduce Combiner规约
1.2.1 数据规约的含义
数据规约是指在尽可能保持数据原貌的前提下,最大限度地精简数据量。
1.2.2 MapReduce弊端
- MapReduce 是一种具有两个执行阶段的分布式计算程序,Map 阶段和 Reduce 阶段之间会涉及到
跨网络数据传递。
- 每一个 MapTask 都可能会产生大量的本地输出,这就导致跨网络传输数据量变大,网络 IO 性能低。
比如 WordCount 单词统计案例,假如文件中有 1000 个单词,其中 999 个为 hello,这将产生 999 个 <hello,1>的键值对在网络中传递,性能及其低下。
1.2.3 Combiner组件概念
Combiner中文叫做数据规约,是 MapReduce 的一种优化手段。- Combiner 的作用就是
对map端的输出先做一次合并,以减少在map和reduce节点之间的数据传输量。
1.2.4 Combiner组件使用
- combiner 是 MapReduce 程序中 Mapper 和 Reducer 之外的一种组件,
默认情况下不启用。
combiner本质就是Reducer,combiner 和 reducer的区别在于运行的位置:
- combiner 是在每一个 maptask 所在的节点运行,是局部聚合;
- Reducer是对所有 maptask 的输出结果计算,是全局聚合;
- 具体实现步骤:
- 自定义一个 CustomCombiner 继承 Reducer,重写 reduce 方法;
- 在 job 中设置:
job.setCombinerClass(CustomCombiner.class);
1.2.5 Combiner使用注意事项
- Combiner 能够应用的前提是不能影响最终的业务逻辑,而且,Combiner 的输出 kv 应该跟 reducer 的输入 kv 类型要对应起来。
- 下述场景禁止使用Combiner,不仅优化了数据量,还改变了最终的结果:
- Combiner 组件不是禁用,而是慎用。
用的好提升程序性能,用不好,改变程序结果且不易发现。
2. MapReduce编程指南
2.1 编程技巧
MapReduce执行流程了然于心,能够知道数据在 MapReduce 中的流转过程。业务需求解读准确,即需要明白做什么。牢牢把握住key的选择,因为 MapReduce 很多行为跟key相关, 比如:排序、分区、分组。- 学会
自定义组件修改默认行为,当默认的行为不满足业务需求,可以尝试自定义规则。
- 通过
画图梳理业务执行流程,确定每个阶段的数据类型。
2.2 MapReduce执行流程图
2.2.1 执行流程图
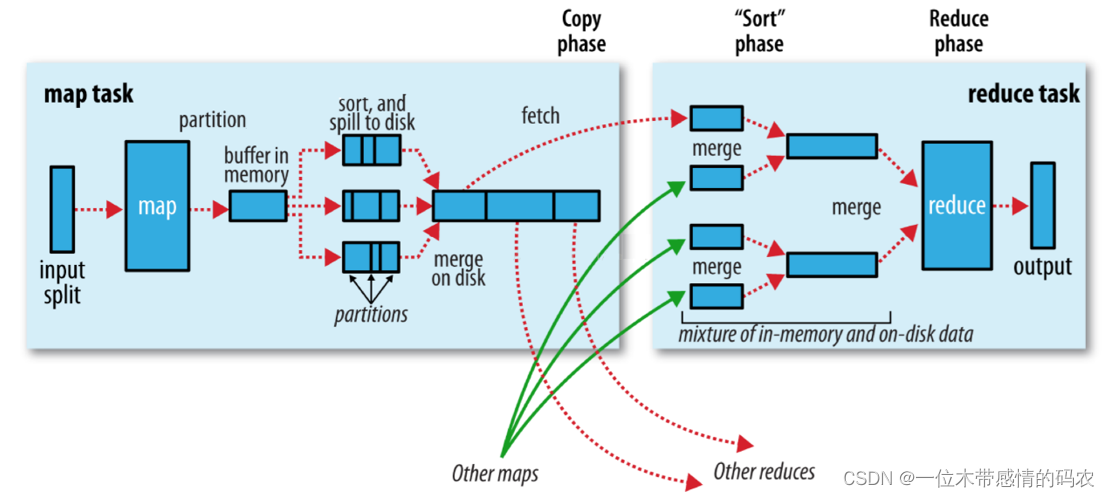
2.2.2 Map阶段执行过程
- 第一阶段是把输入目录下文件按照一定的标准逐个进行
逻辑切片,形成切片规划。默认情况下,Split size=Block size。每一个切片由一个 MapTask 处理(getSplits)。
- 第二阶段是对切片中的数据按照一定的规则
解析成<key,value>对。默认规则是把每一行文本内容解析成键值对。key 是每一行的起始位置(单位是字节),value 是本行的文本内容(TextInputFormat)。
- 第三阶段是调用 Mapper 类中的 map 方法。上阶段中
每解析出来的一个<k,v>,调用一次map方法。每次调用 map 方法会输出零个或多个键值对。
- 第四阶段是按照一定的规则对第三阶段输出的
键值对进行分区。默认是只有一个区。分区的数量就是 Reducer 任务运行的数量。默认只有一个 Reducer 任务。
- 第五阶段是对每个
分区中的键值对进行排序。首先,按照键进行排序,对于键相同的键值对,按照值进行排序。比如三个键值对 <2,2>、<1,3>、<2,1>,键和值分别是整数。那么排序后的结果是 <1,3>、<2,1>、<2,2>。如果有第六阶段,那么进入第六阶段;如果没有,直接输出到文件中。
- 第六阶段是对数据进行
局部聚合处理,也就是 combiner 处理。键相等的键值对会调用一次 reduce 方法。经过这一阶段,数据量会减少。本阶段默认是没有的。
2.2.3 Redue阶段执行过程
- 第一阶段是 Reducer 任务会主动从 Mapper 任务复制其输出的键值对。Mapper 任务可能会有很多,因此 Reducer 会复制多个 Mapper 的输出。
- 第二阶段是把复制到 Reducer 本地数据,全部进行合并,即把分散的数据合并成一个大的数据。再对合并后的数据排序。
- 第三阶段是对排序后的键值对调用 reduce 方法。键相等的键值对调用一次 reduce 方法,每次调用会产生零个或者多个键值对。最后把这些输出的键值对写入到 HDFS 文件中。
2.3 key的重要性体现
- 在 MapReduce 编程中,核心是
牢牢把握住每个阶段的输入输出key是什么。
- 因为 MapReduce 中很多默认行为都跟 key 相关。
排序:key 的字典序a-z 正序分区:key.hashcode % reducetask 个数分组:key 相同的分为一组
- 最重要的是,如果觉得默认的行为不满足业务需求,MapReduce 还支持自定义排序、分区、分组的规则,这将使得编程更加灵活和方便。
3. 案例:美国新冠疫情COVID-19统计
现有美国 2021-1-28 号,各个县 county 的新冠疫情累计案例信息,包括确诊病例和死亡病例,数据格式如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 2021-01-28,Juneau City and Borough,Alaska,02110,1108,3
2021-01-28,Kenai Peninsula Borough,Alaska,02122,3866,18
2021-01-28,Ketchikan Gateway Borough,Alaska,02130,272,1
2021-01-28,Kodiak Island Borough,Alaska,02150,1021,5
2021-01-28,Kusilvak Census Area,Alaska,02158,1099,3
2021-01-28,Lake and Peninsula Borough,Alaska,02164,5,0
2021-01-28,Matanuska-Susitna Borough,Alaska,02170,7406,27
2021-01-28,Nome Census Area,Alaska,02180,307,0
2021-01-28,North Slope Borough,Alaska,02185,973,3
2021-01-28,Northwest Arctic Borough,Alaska,02188,567,1
2021-01-28,Petersburg Borough,Alaska,02195,43,0
|
字段含义如下:date(日期),county(县),state(州),fips(县编码code),cases(累计确诊病例),deaths(累计死亡病例)。
完整数据集链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1AdWWprwEdeyfELOY7YP6ug,提取码:6666
3.1 MapReduce自定义对象序列化
3.1.1 需求
统计美国 2021-1-28,每个州 state 累积确诊案例数、累计死亡案例数。
3.1.2 分析
自定义对象CovidCountBean,用于封装每个县的确诊病例数和死亡病例数。- 注意需要
实现Hadoop的序列化机制。
以州state作为map阶段输出的key,以 CovidCountBean 作为 value,这样经过 MapReduce 的默认排序分组规则,属于同一个州的数据就会变成一组进行 reduce 处理,进行累加即可得出每个州累计确诊病例。
3.1.3 代码实现
3.1.3.1 自定义JavaBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| public class CovidCountBean implements Writable{
private long cases;
private long deaths;
public CovidCountBean() {
}
public CovidCountBean(long cases, long deaths) {
this.cases = cases;
this.deaths = deaths;
}
public void set(long cases, long deaths) {
this.cases = cases;
this.deaths = deaths;
}
public long getCases() {
return cases;
}
public void setCases(long cases) {
this.cases = cases;
}
public long getDeaths() {
return deaths;
}
public void setDeaths(long deaths) {
this.deaths = deaths;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(cases);
out.writeLong(deaths);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.cases = in.readLong();
this.deaths =in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return cases +"\t"+ deaths;
}
}
|
3.1.3.2 Mapper类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class CovidSumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, CovidCountBean> {
Text outKey = new Text();
CovidCountBean outValue = new CovidCountBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] fields = value.toString().split(",");
outKey.set(fields[2]);
outValue.set(Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length-2]),Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length-1]));
context.write(outKey,outValue);
}
}
|
3.1.3.3 Reducer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class CovidSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, CovidCountBean,Text,CovidCountBean> {
CovidCountBean outValue = new CovidCountBean();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<CovidCountBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long totalCases = 0;
long totalDeaths =0;
for (CovidCountBean value : values) {
totalCases += value.getCases();
totalDeaths +=value.getDeaths();
}
outValue.set(totalCases,totalDeaths);
context.write(key,outValue);
}
}
|
3.1.3.4 程序驱动类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class CovidSumDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, CovidSumDriver.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(CovidSumDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(CovidSumMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(CovidSumReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(CovidCountBean.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(CovidCountBean.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
if(fs.exists(new Path(args[1]))){
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]),true);
}
boolean resultFlag = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(resultFlag ? 0 :1);
}
}
|
3.1.4 代码执行结果
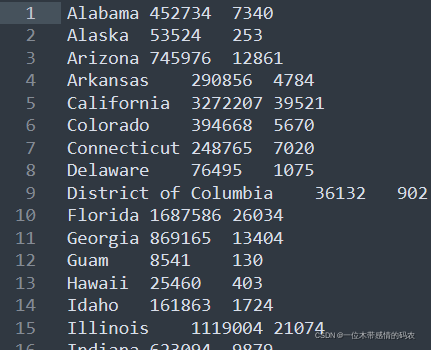
3.2 MapReduce自定义排序
3.2.1 需求
统计美国 2021-01-28,每个州state的累积确证案例数、累积死亡案例数。
将美国 2021-01-28,每个州state的确证案例数进行倒序排序。
3.2.2 分析
如果你的需求中需要根据某个属性进行排序 ,不妨把这个属性作为 key。因为 MapReduce 中key有默认排序行为的。但是需要进行如下考虑:
- 如果你的需求是正序,并且数据类型是 Hadoop 封装好的基本类型。这种情况下不需要任何修改,直接使用基本类型作为 key 即可。因为 Hadoop 封装好的类型已经实现了排序规则。
- 比如,LongWritable 类型:
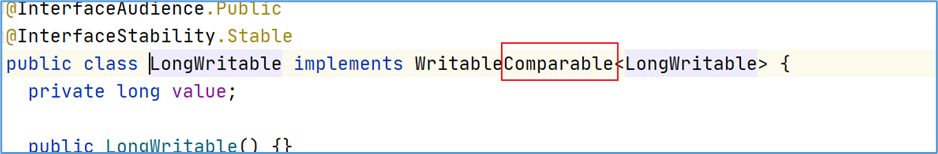
- 如果你的需求是倒序,或者数据类型是自定义对象。需要重写排序规则。需要对象
实现Comparable接口,重写ComparTo方法。

3.2.3 代码实现
3.2.3.1 自定义JavaBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| public class CovidCountBean implements WritableComparable<CovidCountBean> {
private long cases;
private long deaths;
public CovidCountBean() {
}
public CovidCountBean(long cases, long deaths) {
this.cases = cases;
this.deaths = deaths;
}
public void set(long cases, long deaths) {
this.cases = cases;
this.deaths = deaths;
}
public long getCases() {
return cases;
}
public void setCases(long cases) {
this.cases = cases;
}
public long getDeaths() {
return deaths;
}
public void setDeaths(long deaths) {
this.deaths = deaths;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(cases);
out.writeLong(deaths);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.cases = in.readLong();
this.deaths =in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return cases +"\t"+ deaths;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(CovidCountBean o) {
return this.cases - o.getCases()> 0 ? -1:(this.cases - o.getCases() < 0 ? 1 : 0);
}
}
|
3.2.3.2 Mapper类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class CovidSortSumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CovidCountBean,Text> {
CovidCountBean outKey = new CovidCountBean();
Text outValue = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t");
outKey.set(Long.parseLong(fields[1]),Long.parseLong(fields[2]));
outValue.set(fields[0]);
context.write(outKey,outValue);
}
}
|
3.2.3.3 Reducer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class CovidSortSumReducer extends Reducer<CovidCountBean, Text,Text,CovidCountBean> {
@Override
protected void reduce(CovidCountBean key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Text outKey = values.iterator().next();
context.write(outKey,key);
}
}
|
3.2.3.4 驱动程序类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class CovidSortSumDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, CovidSortSumDriver.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(CovidSortSumDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(CovidSortSumMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(CovidSortSumReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CovidCountBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(CovidCountBean.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
if(fs.exists(new Path(args[1]))){
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]),true);
}
boolean resultFlag = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(resultFlag ? 0 :1);
}
}
|
3.2.4 代码执行结果
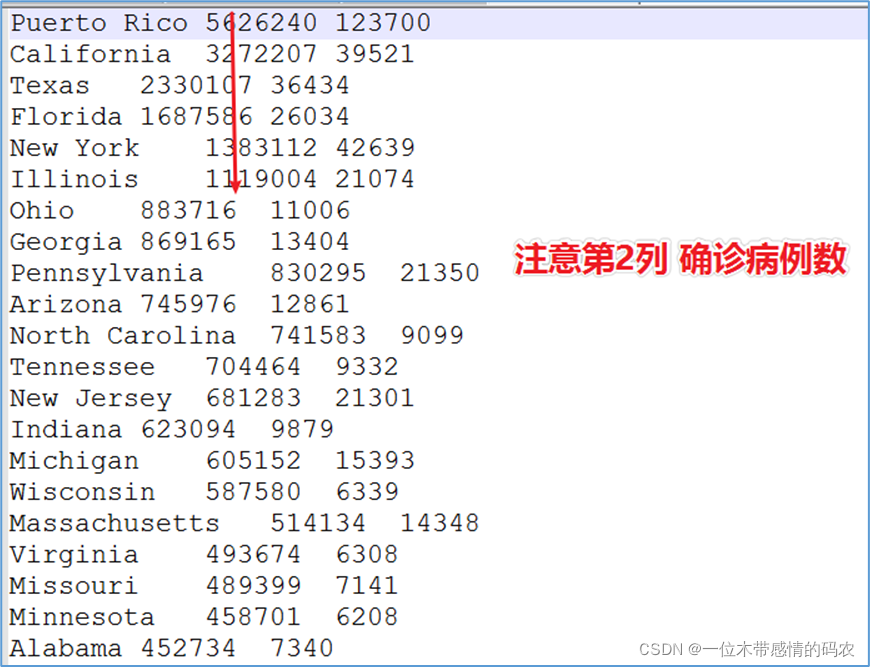
3.3 MapReduce自定义分区
3.3.1 需求
将美国每个州的疫情数据输出到各自不同的文件中,即一个州的数据在一个结果文件中。
3.3.2 分析
输出到不同文件中表示 reducetask 有多个,而 reducetask 默认只有1个,可以通过job.setNumReduceTasks(N)设置。当有多个 reducetask 意味着数据分区,默认分区规则是hashPartitioner,默认分区规则符合业务需求的话,就直接使用;不符合,再自定义分区。
3.3.3 代码实现
3.3.3.1 自定义JavaBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| public class CovidCountBean implements WritableComparable<CovidCountBean> {
private long cases;
private long deaths;
public CovidCountBean() {
}
public CovidCountBean(long cases, long deaths) {
this.cases = cases;
this.deaths = deaths;
}
public void set(long cases, long deaths) {
this.cases = cases;
this.deaths = deaths;
}
public long getCases() {
return cases;
}
public void setCases(long cases) {
this.cases = cases;
}
public long getDeaths() {
return deaths;
}
public void setDeaths(long deaths) {
this.deaths = deaths;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(cases);
out.writeLong(deaths);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.cases = in.readLong();
this.deaths =in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return cases +"\t"+ deaths;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(CovidCountBean o) {
return this.cases - o.getCases()> 0 ? -1:(this.cases - o.getCases() < 0 ? 1 : 0);
}
}
|
3.3.3.2 自定义分区器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public class StatePartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, Text> {
public static HashMap<String, Integer> stateMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
static{
stateMap.put("Alabama", 0);
stateMap.put("Arkansas", 1);
stateMap.put("California", 2);
stateMap.put("Florida", 3);
stateMap.put("Indiana", 4);
}
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, Text value, int numPartitions) {
Integer code = stateMap.get(key.toString());
if (code != null) {
return code;
}
return 5;
}
}
|
3.3.3.3 Mapper类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class CovidPartitionMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text, Text> {
Text outKey = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] splits = value.toString().split(",");
outKey.set(splits[2]);
context.write(outKey,value);
}
}
|
3.3.3.4 Reducer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class CovidPartitionReducer extends Reducer<Text,Text,Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(value,NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
|
3.3.3.5 驱动程序类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| public class CovidPartitionDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, CovidPartitionDriver.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(CovidPartitionDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(CovidPartitionMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(CovidPartitionReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(6);
job.setPartitionerClass(StatePartitioner.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
if(fs.exists(new Path(args[1]))){
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]),true);
}
boolean resultFlag = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(resultFlag ? 0 :1);
}
}
|
3.3.4 代码执行结果
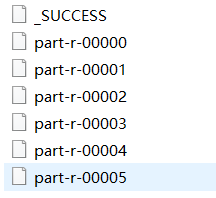
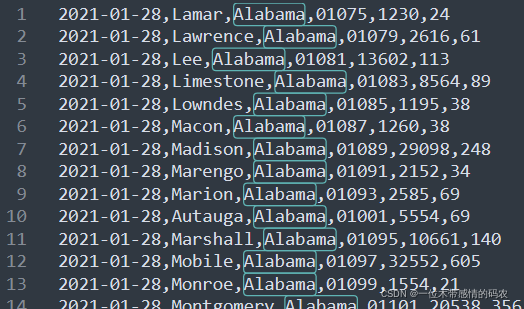
3.3.5 分区个数和reducetask个数的关系
正常情况下:分区的个数 = reducetask个数
- 分区的个数 > reducetask个数
- 分区的个数 < reducetask个数
3.4 MapReduce自定义分组
3.4.1 分组概念和默认分组规则
- 分组在发生在 reduce 阶段,决定了
同一个reduce中哪些数据将组成一组去调用reduce方法处理。
- 默认分组规则是:
key相同的就会分为一组(前后两个 key 直接比较是否相等)。
- 需要注意的是,在 reduce 阶段进行分组之前,因为进行数据排序行为,因此
排序+分组将会使得key一样的数据一定被分到同一组,一组去调用reduce方法处理。
3.4.2 自定义分组规则
- 写类继承WritableComparator,重写Compare方法。
- 只要
Compare方法返回为 0,MapReduce框架在分组的时候就会认为前后两个相等,分为一组。
- 在 job 对象中进行设置才能让自己的重写分组类生效:
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(xxxx.class);
3.4.3 需求
找出美国 2021-01-28,每个州 state 的确诊案例数最多的县 county 是哪一个。该问题也是俗称的 TopN 问题。
3.4.4 分析
- 在 ma p阶段将 “州state和累计确诊病例数cases” 作为 key 输出;
- 重写对象的排序规则,
首先根据州的正序排序,如果州相等,按照确诊病例数cases倒序排序,发送到 reduce;
- 在 reduce 端利用自定义分组规则,将
州state相同的分为一组,然后取第一个即是最大值;
3.4.5 代码实现
3.4.5.1 自定义对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| public class CovidBean implements WritableComparable<CovidBean> {
private String state;
private String county;
private long cases;
public CovidBean() {
}
public CovidBean(String state, String county, long cases) {
this.state = state;
this.county = county;
this.cases = cases;
}
public void set (String state, String county, long cases) {
this.state = state;
this.county = county;
this.cases = cases;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getCounty() {
return county;
}
public void setCounty(String county) {
this.county = county;
}
public long getCases() {
return cases;
}
public void setCases(long cases) {
this.cases = cases;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CovidBean{" +
"state='" + state + '\'' +
", county='" + county + '\'' +
", cases=" + cases +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(CovidBean o) {
int result ;
int i = state.compareTo(o.getState());
if ( i > 0) {
result =1;
} else if (i <0 ) {
result = -1;
} else {
result = cases > o.getCases() ? -1 : 1;
}
return result;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(state);
out.writeUTF(county);
out.writeLong(cases);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.state =in.readUTF();
this.county =in.readUTF();
this.cases =in.readLong();
}
}
|
3.4.5.2 Mapper类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class CovidTop1Mapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CovidBean, NullWritable> {
CovidBean outKey = new CovidBean();
NullWritable outValue = NullWritable.get();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] fields = value.toString().split(",");
outKey.set(fields[2],fields[1],Long.parseLong(fields[4]));
context.write(outKey,outValue);
}
}
|
3.4.5.3 Reducer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class CovidTop1Reducer extends Reducer<CovidBean, NullWritable,CovidBean,NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(CovidBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key,NullWritable.get());
}
}
|
3.4.5.4 自定义分组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class CovidGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator {
protected CovidGroupingComparator(){
super(CovidBean.class,true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
CovidBean aBean = (CovidBean) a;
CovidBean bBean = (CovidBean) b;
return aBean.getState().compareTo(bBean.getState());
}
}
|
3.4.5.5 驱动程序类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| public class CovidTop1Driver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, CovidTop1Driver.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(CovidTop1Driver.class);
job.setMapperClass(CovidTop1Mapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(CovidTop1Reducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CovidBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(CovidBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(CovidGroupingComparator.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
if(fs.exists(new Path(args[1]))){
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]),true);
}
boolean resultFlag = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(resultFlag ? 0 :1);
}
}
|
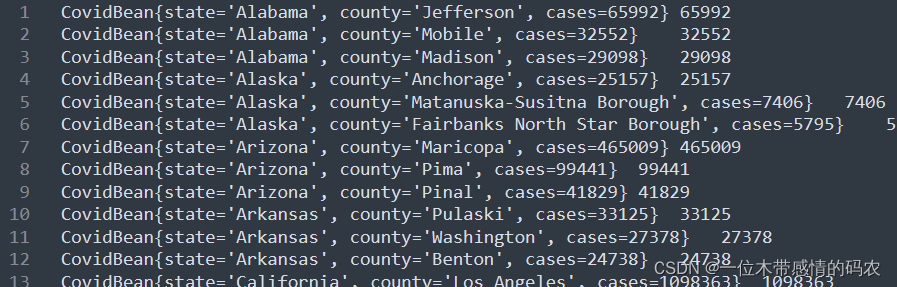
3.4.6 代码执行结果
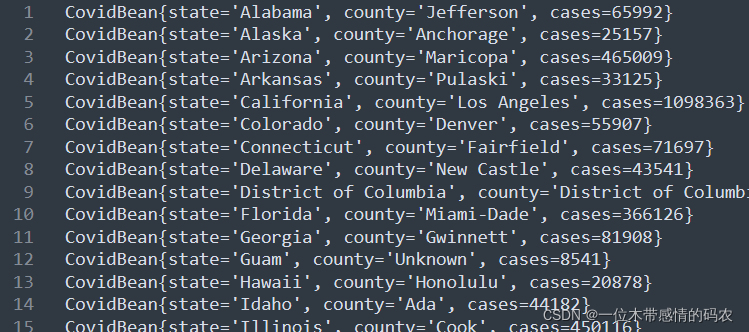
3.5 自定义分组扩展:topN问题
3.5.1 需求
找出美国 2021-01-28,每个州 state 的确诊案例数最多的县 county 前 3 个。(Top3 问题)
3.5.2 分析
- 在 map 阶段将 “州state和累计确诊病例数cases” 作为 key 输出;
- 重写对象的排序规则,
首先根据州的正序排序,如果州相等,按照确诊病例数cases倒序排序,发送到 reduce;
- 在 reduce 端利用自定义分组规则,将
州state相同的分为一组,然后遍历取值,取出每组中的前 3 个即可。
为了验证验证结果方便,可以在输出的时候以 cases 作为 value,实际上为空即可,value 并无实际意义。
3.5.3 代码实现
3.5.3.1 自定义对象、自定义分组类
这两个和上述的 Top1 一样,此处就不再重复编写。可以直接使用。
3.5.3.2 Mapper类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class CovidTopNMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CovidBean,LongWritable> {
CovidBean outKey = new CovidBean();
LongWritable outValue = new LongWritable();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] fields = value.toString().split(",");
outKey.set(fields[2],fields[1],Long.parseLong(fields[4]));
outValue.set(Long.parseLong(fields[4]));
context.write(outKey,outValue);
}
}
|
3.5.3.3 Reducer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class CovidTopNReducer extends Reducer<CovidBean, LongWritable,CovidBean,LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(CovidBean key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int num =0;
for (LongWritable value : values) {
if(num < 3 ){
context.write(key,value);
num++;
}else{
return;
}
}
}
}
|
3.5.3.4 程序驱动类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public class CovidTopNDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, CovidTopNDriver.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(CovidTopNDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(CovidTopNMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(CovidTopNReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CovidBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(CovidBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(CovidGroupingComparator.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
if(fs.exists(new Path(args[1]))){
fs.delete(new Path(args[1]),true);
}
boolean resultFlag = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(resultFlag ? 0 :1);
}
}
|
3.5.4 代码执行结果