Hadoop 生态圈(十四)- HDFS 小文件解决方案 | 字数总计: 2.9k | 阅读时长: 12分钟 | 阅读量:
前言
部分内容摘自尚硅谷、黑马等培训资料
1. Hadoop Archive归档
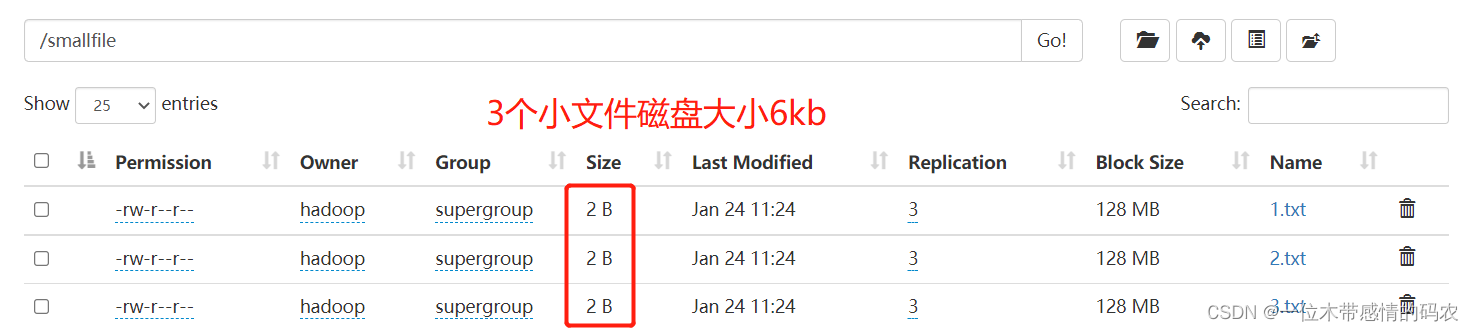
HDFS 并不擅长存储小文件,因为每个文件最少一个 block,每个 block 的元数据都会在 NameNode 占用内存,如果存在大量的小文件,它们会吃掉 NameNode 节点的大量内存。如下所示,模拟小文件场景:
1 2 3 4 5 [hadoop@hadoop1 input]$ hadoop fs -mkdir /smallfile [hadoop@hadoop1 input]$ echo 1 > 1.txt [hadoop@hadoop1 input]$ echo 2 > 2.txt [hadoop@hadoop1 input]$ echo 3 > 3.txt [hadoop@hadoop1 input]$ hadoop fs -put 1.txt 2.txt 3.txt /smallfile
Hadoop Archives可以有效的处理以上问题,它可以把多个文件归档成为一个文件,归档成一个文件后还可以透明的访问每一个文件。
1.1 创建Archive
Usage: hadoop archive -archiveName name -p <parent> <src>* <dest>-archiveName是指要创建的存档的名称。比如test.har,archive 的名字的扩展名应该是*.har。 -p参数指定文件存档文件(src)的相对路径。-p /foo/bar a/b/c e/f/g,这里的/foo/bar是a/b/c与e/f/g的父路径,所以完整路径为/foo/bar/a/b/c与/foo/bar/e/f/g。/smallfile下的所有文件:hadoop archive -archiveName test.har -p /smallfile /outputdir/outputdir目录下创建一个名为test.har的存档文件。注意:
1.2 查看Archive
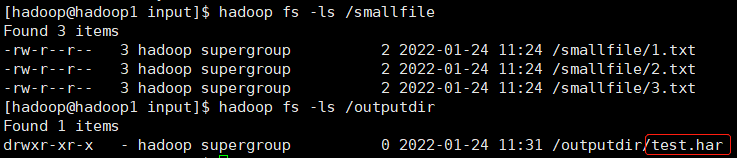
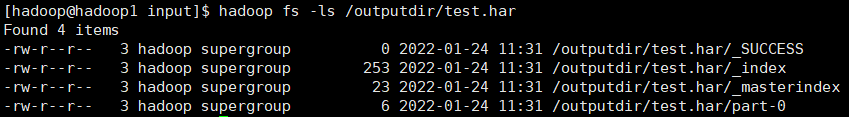
1.2.1 查看归档之后的样子
首先我们来看下创建好的 har 文件。使用如下的命令:hadoop fs -ls /outputdir/test.harpart文件是多个原文件的集合, 通过 index 文件可以去找到原文件。
1.2.2 查看归档之前的样子
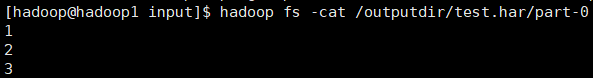
在查看 har 文件的时候,如果没有指定访问协议,默认使用的就是 hdfs://,此时所能看到的就是归档之后的样子。用har uri去访问的话,索引、标识等文件就会隐藏起来,只显示创建档案之前的原文件:har://scheme-hostname:port/archivepath/fileinarchive hdfs-域名:端口
1 2 3 hadoop fs -ls har://hdfs-node1:8020/outputdir/test.har/ hadoop fs -ls har:///outputdir/test.har hadoop fs -cat har:///outputdir/test.har/1.txt
1.3 提取Archive
按顺序解压存档(串行):hadoop fs -cp har:///user/zoo/foo.har/dir1 hdfs:/user/zoo/newdir
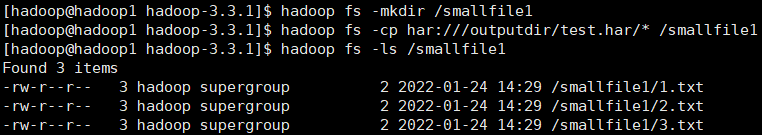
1 2 3 hadoop fs -mkdir /smallfile1 hadoop fs -cp har:///outputdir/test.har/* /smallfile1 hadoop fs -ls /smallfile1
hadoop distcp har:///user/zoo/foo.har/dir1 hdfs:/user/zoo/newdir
1 hadoop distcp har:///outputdir/test.har/* /smallfile2
1.4 Archive使用注意事项
Hadoop archives 是特殊的档案格式。一个 Hadoop archive 对应一个文件系统目录。Hadoop archive 的扩展名是*.har;
创建 archives 本质是运行一个 Map/Reduce 任务,所以应该在 Hadoop 集群上运行创建档案的命令;
创建 archive 文件要消耗和原文件一样多的硬盘空间;
archive 文件不支持压缩,尽管 archive 文件看起来像已经被压缩过;
archive 文件一旦创建就无法改变,要修改的话,需要创建新的 archive 文件。事实上,一般不会再对存档后的文件进行修改,因为它们是定期存档的,比如每周或每日;
当创建 archive 时,源文件不会被更改或删除;
2. Sequence File
2.1 Sequence File介绍
Sequence File是 Hadoop API 提供的一种二进制文件支持。这种二进制文件直接将<key, value>键值对序列化到文件中。
2.2 Sequence File优缺点
优点
二级制格式存储,比文本文件更紧凑。
支持不同级别压缩(基于 Record 或 Block 压缩)。
文件可以拆分和并行处理,适用于 MapReduce。
缺点
二进制格式文件不方便查看。
特定于 hadoop,只有 Java API 可用于与之件进行交互。尚未提供多语言支持。
2.3 Sequence File格式
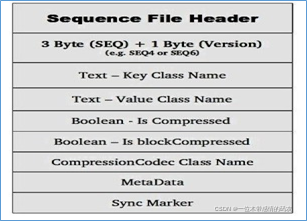
Hadoop Sequence File 是一个由二进制键/值对组成的。根据压缩类型,有 3 种不同的 Sequence File 格式:未压缩格式、record压缩格式、block压缩格式。header和一个或多个record组成。以上三种格式均使用相同的 header 结构,如下所示:
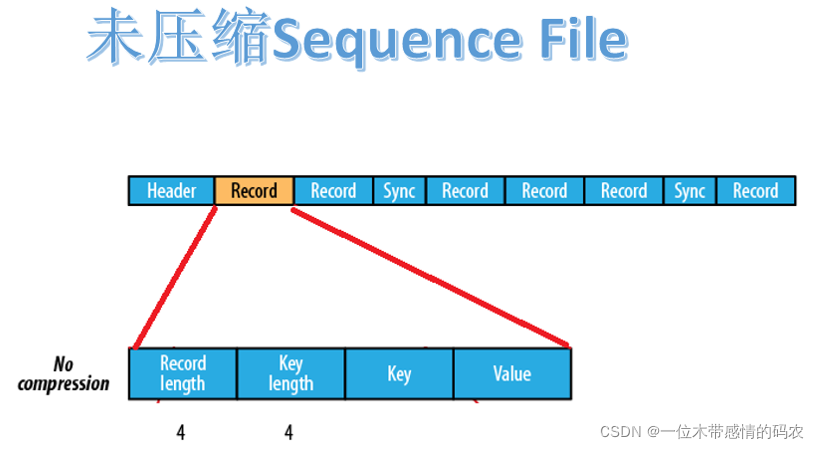
2.3.1 未压缩格式
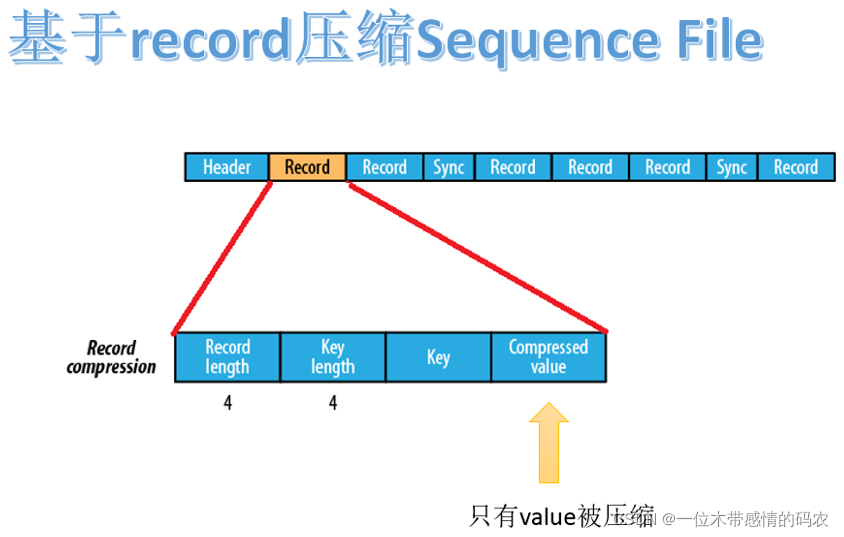
2.3.2 基于record压缩格式
compressed value(被压缩的值)。
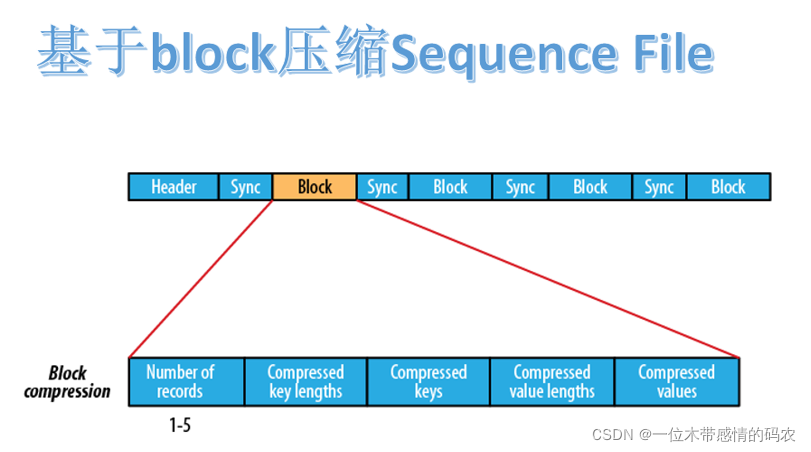
2.3.3 基于block压缩格式
block指的是record block,可以理解为多个record记录组成的块。注意,这个 block 和 HDFS 中分块存储的 block(128M)是不同的概念。
2.4 Sequence File文件读写
2.4.1 开发环境构建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.hadoop</groupId > <artifactId > hadoop-common</artifactId > <version > 3.3.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.hadoop</groupId > <artifactId > hadoop-hdfs</artifactId > <version > 3.3.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.hadoop</groupId > <artifactId > hadoop-client</artifactId > <version > 3.3.1</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
2.4.2 SequenceFileWrite
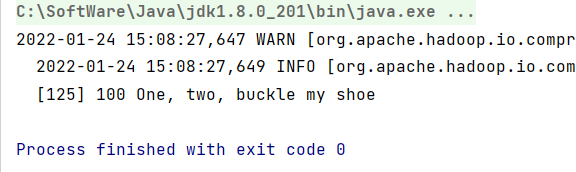
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import java.net.URI;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionCodec;import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec;public class SequenceFileWrite { private static final String[] DATA = { "One, two, buckle my shoe" , "Three, four, shut the door" , "Five, six, pick up sticks" , "Seven, eight, lay them straight" , "Nine, ten, a big fat hen" }; public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME" ,"hadoop" ); Configuration conf = new Configuration (); IntWritable key = new IntWritable (); Text value = new Text (); SequenceFile.Writer writer = null ; CompressionCodec Codec = new GzipCodec (); SequenceFile.Writer.Option optPath = SequenceFile.Writer.file(new Path ("hdfs://192.168.68.101:8020/seq.out" )); SequenceFile.Writer.Option optKey = SequenceFile.Writer.keyClass(key.getClass()); SequenceFile.Writer.Option optVal = SequenceFile.Writer.valueClass(value.getClass()); SequenceFile.Writer.Option optCom = SequenceFile.Writer.compression(SequenceFile.CompressionType.RECORD,Codec); try { writer = SequenceFile.createWriter( conf, optPath, optKey, optVal, optCom); for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) { key.set(100 - i); value.set(DATA[i % DATA.length]); System.out.printf("[%s]\t%s\t%s\n" , writer.getLength(), key, value); writer.append(key, value); } } finally { IOUtils.closeStream(writer); } } }
运行结果:
2.4.3 SequenceFileRead
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;import org.apache.hadoop.util.ReflectionUtils;import java.io.IOException;public class SequenceFileRead { public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME" ,"hadoop" ); Configuration conf = new Configuration (); SequenceFile.Reader.Option option1 = SequenceFile.Reader.file(new Path ("hdfs://192.168.68.101:8020/seq.out" )); SequenceFile.Reader.Option option2 = SequenceFile.Reader.length(174 ); SequenceFile.Reader reader = null ; try { reader = new SequenceFile .Reader(conf,option1,option2); Writable key = (Writable) ReflectionUtils.newInstance( reader.getKeyClass(), conf); Writable value = (Writable) ReflectionUtils.newInstance( reader.getValueClass(), conf); long position = reader.getPosition(); while (reader.next(key, value)) { String syncSeen = reader.syncSeen() ? "*" : "" ; System.out.printf("[%s%s]\t%s\t%s\n" , position, syncSeen, key, value); position = reader.getPosition(); } } finally { IOUtils.closeStream(reader); } } }
运行结果:
2.5 案例:使用Sequence File合并小文件
2.5.1 理论依据
可以使用 Sequence File 对小文件合并,即将文件名作为key,文件内容作为value序列化到大文件中。例如,假设有 10,000 个 100KB 文件,那么我们可以编写一个程序将它们放入单个 Sequence File 中,如下所示,可以在其中使用 filename 作为键,并使用 content 作为值。
2.5.2 具体值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.nio.charset.Charset;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.DigestUtils;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileUtil;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.BytesWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile;import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile.Reader;import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile.Writer;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;public class MergeSmallFilesToSequenceFile { private Configuration configuration = new Configuration (); private List<String> smallFilePaths = new ArrayList <String>(); public void addInputPath (String inputPath) throws Exception{ File file = new File (inputPath); if (file.isDirectory()){ File[] files = FileUtil.listFiles(file); for (File sFile:files){ smallFilePaths.add(sFile.getPath()); System.out.println("添加小文件路径:" + sFile.getPath()); } }else { smallFilePaths.add(file.getPath()); System.out.println("添加小文件路径:" + file.getPath()); } } public void mergeFile () throws Exception{ Writer.Option bigFile = Writer.file(new Path ("D:\\datasets\\bigfile" )); Writer.Option keyClass = Writer.keyClass(Text.class); Writer.Option valueClass = Writer.valueClass(BytesWritable.class); Writer writer = SequenceFile.createWriter(configuration, bigFile, keyClass, valueClass); Text key = new Text (); for (String path:smallFilePaths){ File file = new File (path); long fileSize = file.length(); byte [] fileContent = new byte [(int )fileSize]; FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream (file); inputStream.read(fileContent, 0 , (int )fileSize); String md5Str = DigestUtils.md5Hex(fileContent); System.out.println("merge小文件:" +path+",md5:" +md5Str); key.set(path); writer.append(key, new BytesWritable (fileContent)); } writer.hflush(); writer.close(); } public void readMergedFile () throws Exception{ Reader.Option file = Reader.file(new Path ("D:\\bigfile.seq" )); Reader reader = new Reader (configuration, file); Text key = new Text (); BytesWritable value = new BytesWritable (); while (reader.next(key, value)){ byte [] bytes = value.copyBytes(); String md5 = DigestUtils.md5Hex(bytes); String content = new String (bytes, Charset.forName("GBK" )); System.out.println("读取到文件:" +key+",md5:" +md5+",content:" +content); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { MergeSmallFilesToSequenceFile msf = new MergeSmallFilesToSequenceFile (); msf.addInputPath("D:\\datasets\\smallfile" ); msf.mergeFile(); } }